Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) therapy is a cornerstone in treating respiratory distress in neonates. Two prominent variations of CPAP—bubble CPAP and Nasal CPAP (nCPAP)—offer unique advantages and are widely used in neonatal intensive care units (NICUs) worldwide. This blog delves into the specifics of Bubble CPAP and nCPAP, their mechanisms, benefits, and applications, with a special mention of B&B Medical Technologies, a leader in respiratory support solutions.
What is Bubble CPAP?
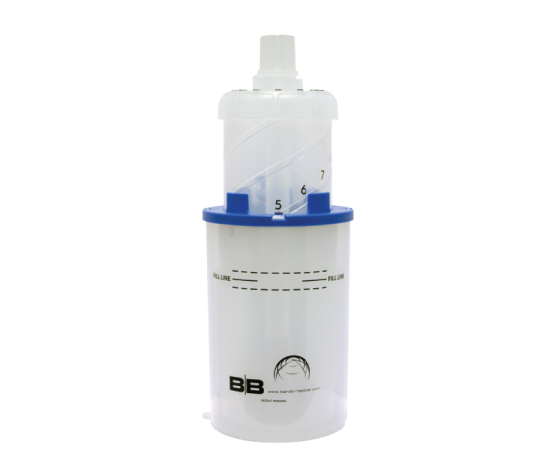
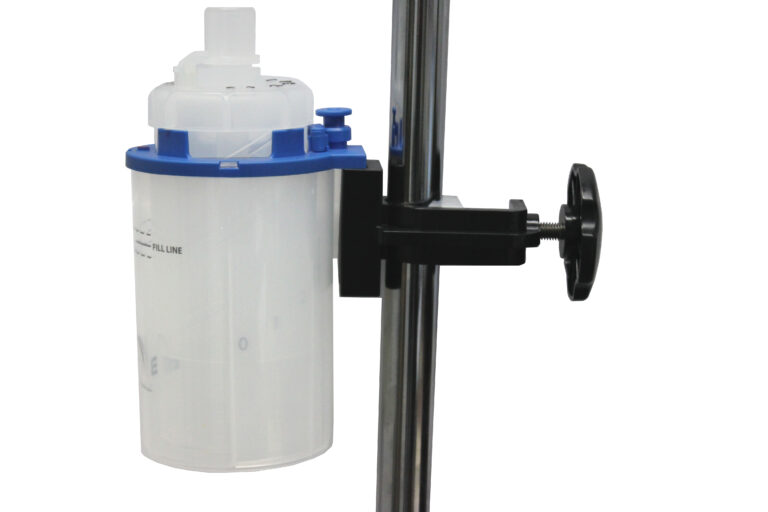
Bubble CPAP is a non-invasive ventilation strategy designed to support the breathing of preterm and term infants experiencing respiratory distress. This method delivers continuous positive airway pressure to the infant’s lungs through a nasal interface, typically prongs or a mask. The pressure is generated by a constant flow of air or oxygen, which passes through a tube submerged in water, creating bubbles that maintain the desired pressure level.
Mechanism of Bubble CPAP
The primary mechanism of Bubble CPAP lies in its simplicity and effectiveness. The bubbling in the water column provides a gentle, oscillating pressure that helps keep the infant’s airways open, preventing alveolar collapse and improving gas exchange. This oscillation mimics the natural variability of breathing, which can be particularly beneficial for neonates with immature respiratory systems. Additionally, the water column acts as a pressure regulator, ensuring consistent delivery of the therapeutic pressure.
Benefits of Bubble CPAP
Bubble CPAP offers several key benefits:
- Non-invasive Support: Bubble CPAP is a noninvasive technique that reduces the need for intubation and mechanical ventilation, minimizing the risk of lung injury and infection.
- Ease of Use: The system is relatively simple to set up and adjust, making it accessible for healthcare providers in various settings.
- Cost-Effective: Bubble CPAP is cost-effective and requires minimal maintenance compared to more complex mechanical ventilation systems.
- Physiological Benefits: The gentle oscillations and consistent pressure support the infant’s natural breathing patterns, enhancing overall respiratory function and comfort.
Understanding nCPAP
Nasal CPAP (nCPAP) is another noninvasive respiratory support method commonly used in NICUs. Unlike Bubble CPAP, nCPAP typically involves using a mechanical device to generate and maintain positive airway pressure, delivered through nasal prongs or a mask.
Mechanism of nCPAP
In nCPAP, a machine continuously pushes air or oxygen into the infant’s airways. This constant pressure helps open the alveoli, preventing collapse and promoting better oxygenation and carbon dioxide removal. nCPAP devices often have advanced features, such as pressure monitoring and alarm systems, ensuring precise control and safety.
Benefits of nCPAP
Nasal CPAP also presents numerous benefits:
- Precision and Control: A mechanical device allows for precise adjustment of pressure levels tailored to the infant’s specific needs.
- Monitoring Capabilities: Advanced nCPAP machines include monitoring systems that provide real-time data on pressure, oxygen levels, and the infant’s breathing patterns, enhancing clinical decision-making.
- Adaptability: nCPAP systems can be adjusted to various pressure levels and flow rates, making them suitable for multiple respiratory conditions.
- Reduced Work of Breathing: By providing continuous positive pressure, nCPAP reduces the effort required by the infant to breathe, conserving energy and promoting growth and development.
Conclusion
Bubble CPAP and nCPAP are vital non-invasive respiratory support techniques crucial in neonatal care. Each method offers unique advantages, from the simplicity and cost-effectiveness of Bubble CPAP to the precision and adaptability of nCPAP. B&B Medical Technologies stands out as a key player in this field, providing top-tier solutions that enhance the quality of care for infants with respiratory distress. As neonatal care continues to evolve, these technologies will remain indispensable in ensuring the health and well-being of newborns.