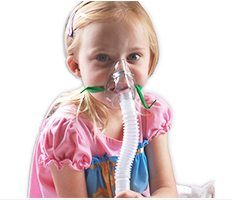
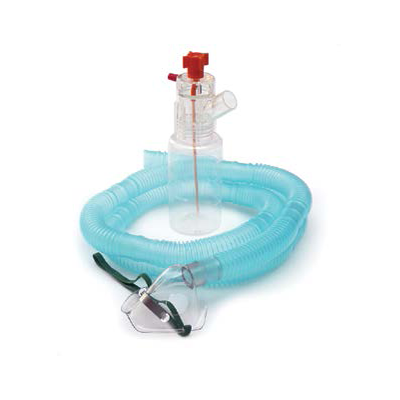
Nebulizers are essential medical devices commonly used to administer medicines to people who have chronic respiratory illnesses, like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, and other lung diseases. Whether at home or in a healthcare setting, they have an important role to play in helping you maintain your respiratory health. In this blog, we will explore what a nebulizing machine is, its types, uses, cleaning procedures, and more, so you can better understand how this device works and its importance in respiratory care.
What is a Nebulizer?
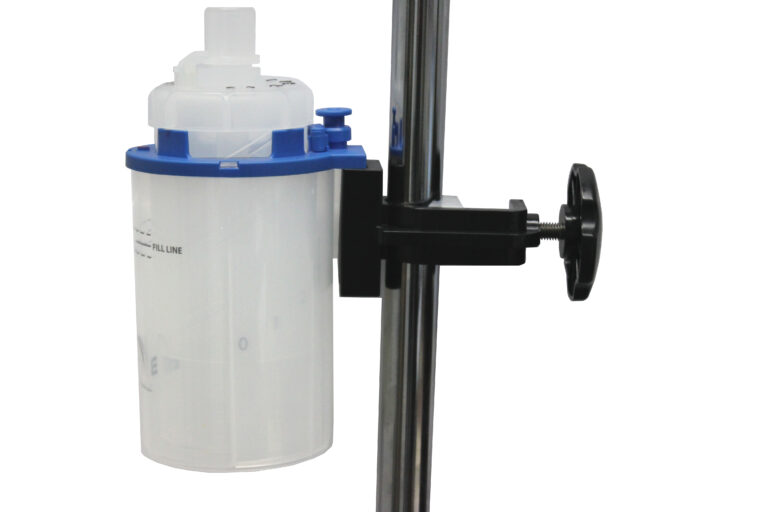
It is a machine which turns liquid medicine into a thin mist, which you can inhale directly into your lungs. This process helps the medication work faster and more efficiently, particularly for individuals who struggle to use inhalers effectively. The mist produced by the nebulizing machine is easy to inhale and provides relief to those suffering from respiratory ailments.
These machines are commonly prescribed for patients with conditions like asthma, bronchitis, and COPD. They have several types, each made to fulfill specific medical needs.
Types of Nebulizing Machines
1. Compressor Nebulizers
These are the most commonly used type of nebulizer machines. They work by using compressed air to turn liquid medicine into a fine mist. Compressor units are typically larger and require a power source, making them ideal for home use.
2. Ultrasonic Nebulizers
These use sound waves to break the medicine into a fine mist. These are typically quieter than compressor models, which makes them a good option for use in settings where noise may be a concern, such as at night.
3. Mesh Nebulizers
The mesh nebulizing machines are compact and portable devices that use a vibrating mesh to generate a mist. They are usually smaller, quieter, and faster than both compressor and ultrasonic models. These are highly recommended for travel or when you need a discreet way to administer medication.
Nebulizer Uses
Nebulizing machines are mainly used to administer nebulizer liquid, which contains medications like bronchodilators, corticosteroids, or antibiotics. The primary nebulizer uses are for managing diseases which affect your airways and lungs, like:
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): Nebulizing machines are used to deliver medication that helps open the airways in individuals with COPD, allowing for better airflow.
- Asthma: Nebulizing machines help manage this ailment by providing bronchodilators which relax muscles around your airways, making it easier for you to breath.
- Cystic Fibrosis: For those with cystic fibrosis, nebulizing machines can help administer mucus-thinning medication to clear the airways and improve lung function.
- Acute Respiratory Conditions: In cases of pneumonia or other acute respiratory conditions, they are used to deliver antibiotics or other medications to fight infections.
How to Clean a Nebulizer
Proper cleaning is very important to make sure that your nebulizing machine continues to function effectively and remains free from bacteria or mold buildup. Here’s a simple guide to cleaning your nebulizing machine:
- Disassemble the Parts: After each use, separate the nebulizer cup, tubing, and mask or mouthpiece.
- Wash with Warm Soapy Water: Rinse the parts with soapy, warm water to remove any remaining medicine. Don’t use harsh cleaning solutions having chemicals in them as that could destroy the device.
- Rinse Thoroughly: After washing, rinse the parts with clean water to remove soap residue.
- Air Dry: Allow the parts to air dry completely on a clean towel or surface before reassembling.
- Disinfect Weekly: Once a week, disinfect the nebulizer parts using a solution recommended by your manufacturer. This will help prevent germs from growing in the device.
How to Use it
Using a nebulizer machine is easy and straightforward. Here’s how to use it properly:
- Prepare the Medication: Follow your doctor’s instructions for measuring the prescribed nebulizer liquid.
- Connect the Nebulizer to the Power Source: If you are using a compressor unit, plug it into the power source. For portable nebulizing machine , ensure that the battery is charged.
- Place the Medicine in the Nebulizer Cup: Pour the prescribed amount of nebulizer liquid into the nebulizer cup. Connect the cup to the tubing.
- Inhale the Mist: Put the mouthpiece into your mouth or mask over your mouth and nose. Turn on the nebulizing machine and inhale deeply through your mouth until the mist stops. This usually takes about 10 to 15 minutes.
- Turn off and Clean: Once the treatment is complete, turn off the machine and clean it according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
It turns liquid medicine into a thin mist which you can inhale directly into your lungs, helping to relieve symptoms of respiratory conditions.
Yes, a prescription is typically required for purchasing a nebulizing machine as it is a medical device used for treating specific respiratory conditions.
Yes, nebulizing helps deliver medication directly to the lungs, providing quicker relief for respiratory conditions such as asthma and COPD.
After nebulizing, avoid eating, drinking, or exercising for about 30 minutes to allow the medication to work effectively.
The Bottom Line
A nebulizer is an effective and easy-to-use medical device that provides essential help for individuals with respiratory conditions. It makes sure that the medicine gets into your lungs quickly, making it an invaluable tool in healing respiratory diseases such as COPD and asthma. If you are in need of a reliable nebulizer machine, Visit B&B Medical Technologies for high-quality and clinically proven nebulizers and related products.
By following the proper cleaning and usage procedures, you can ensure your nebulizer operates at its best, helping you manage your respiratory health more effectively. For more information about nebulizers and our full range of medical devices, feel free to reach out to us at B&B Medical Technologies.